Dual-axis Combo Chart in Python
Contents
4.4. Dual-axis Combo Chart in Python#
This is a Notebook for the medium article Creating a dual-axis Combo Chart in Python
Please check out article for instructions
License: BSD 2-Clause
4.4.1. Version of packages used in this Notebook#
%%capture
!pip install seaborn
import matplotlib as m
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# Make sure your package version >= them
print('matplotlib: ', m.__version__)
print('numpy: ', np.__version__)
print('pandas: ', pd.__version__)
matplotlib: 3.6.0
numpy: 1.23.2
pandas: 1.5.0
4.5. Tutorial#
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
plt.style.use('seaborn')
# Needed for jupyter notebooks
%matplotlib inline
%config InlineBackend.figure_format = 'retina'
# Default figure size: 8 by 5
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = (8, 5)
/var/folders/rp/c0_pxspj11g3dzxkc_qfxvdr0000gn/T/ipykernel_90922/2310884817.py:1: MatplotlibDeprecationWarning: The seaborn styles shipped by Matplotlib are deprecated since 3.6, as they no longer correspond to the styles shipped by seaborn. However, they will remain available as 'seaborn-v0_8-<style>'. Alternatively, directly use the seaborn API instead.
plt.style.use('seaborn')
x = ['Jan', 'Feb', 'Mar', 'Apr', 'May', 'Jun', 'Jul', 'Aug', 'Sep', 'Oct', 'Nov', 'Dec']
#https://en.climate-data.org/europe/germany/bremen/bremen-82/
#1991-2021
average_temp = [2.3, 2.6, 5.2, 9.5, 13.5, 16.4, 18.5, 18.1, 15.1, 10.9, 6.4, 3.4]
average_precipitation_mm = [71, 54, 58, 55, 64, 74, 84, 79, 65, 65, 62, 70]
bremen_climate = pd.DataFrame(
{
'average_temp': average_temp,
'average_precipitation_mm': average_precipitation_mm
},
index=x
)
bremen_climate
| average_temp | average_precipitation_mm | |
|---|---|---|
| Jan | 2.3 | 71 |
| Feb | 2.6 | 54 |
| Mar | 5.2 | 58 |
| Apr | 9.5 | 55 |
| May | 13.5 | 64 |
| Jun | 16.4 | 74 |
| Jul | 18.5 | 84 |
| Aug | 18.1 | 79 |
| Sep | 15.1 | 65 |
| Oct | 10.9 | 65 |
| Nov | 6.4 | 62 |
| Dec | 3.4 | 70 |
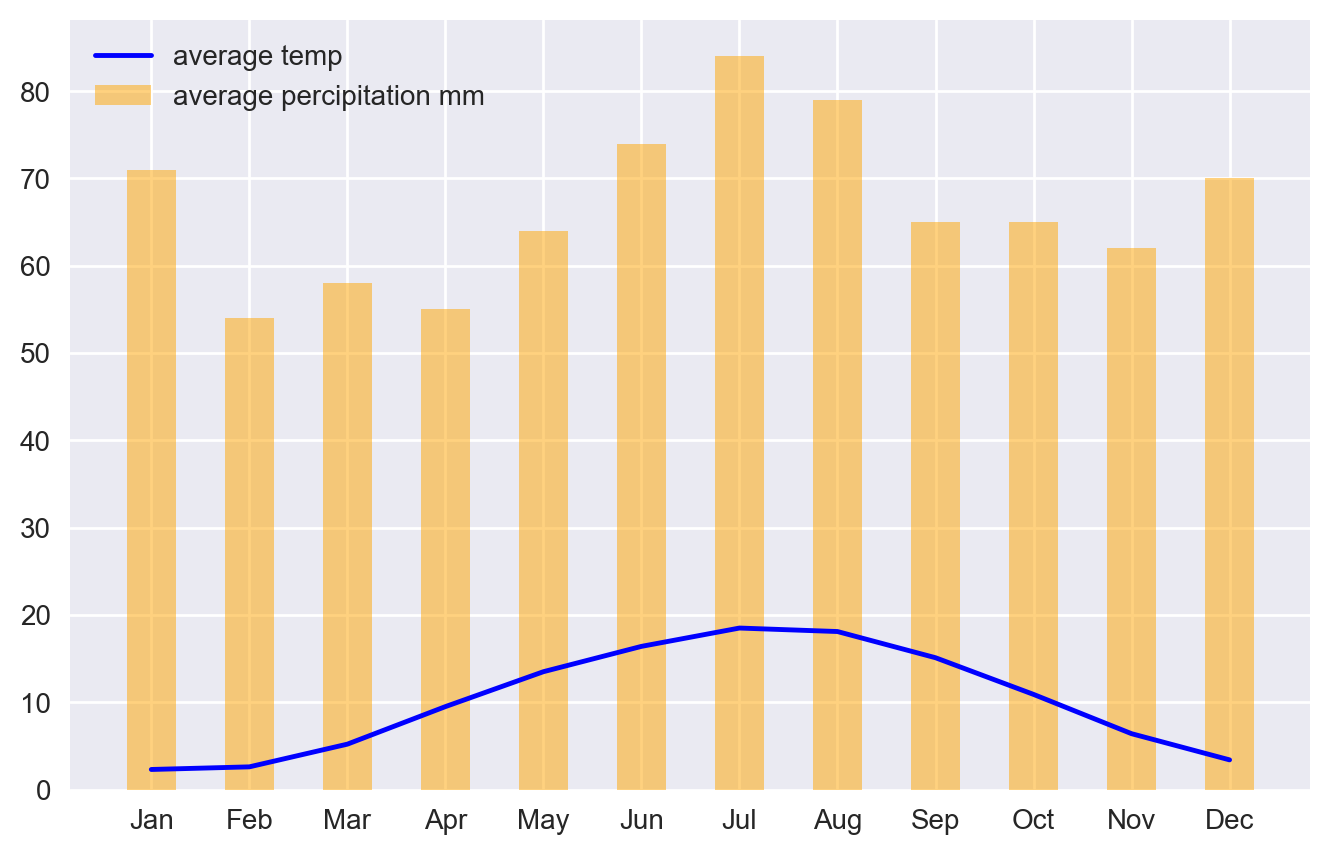
4.5.1. 1. Problem using the same axis#
plt.plot(x, average_temp, "-b", label="average temp")
plt.bar(x, average_precipitation_mm, width=0.5, alpha=0.5, color='orange', label="average percipitation mm", )
plt.legend(loc="upper left")
plt.show()
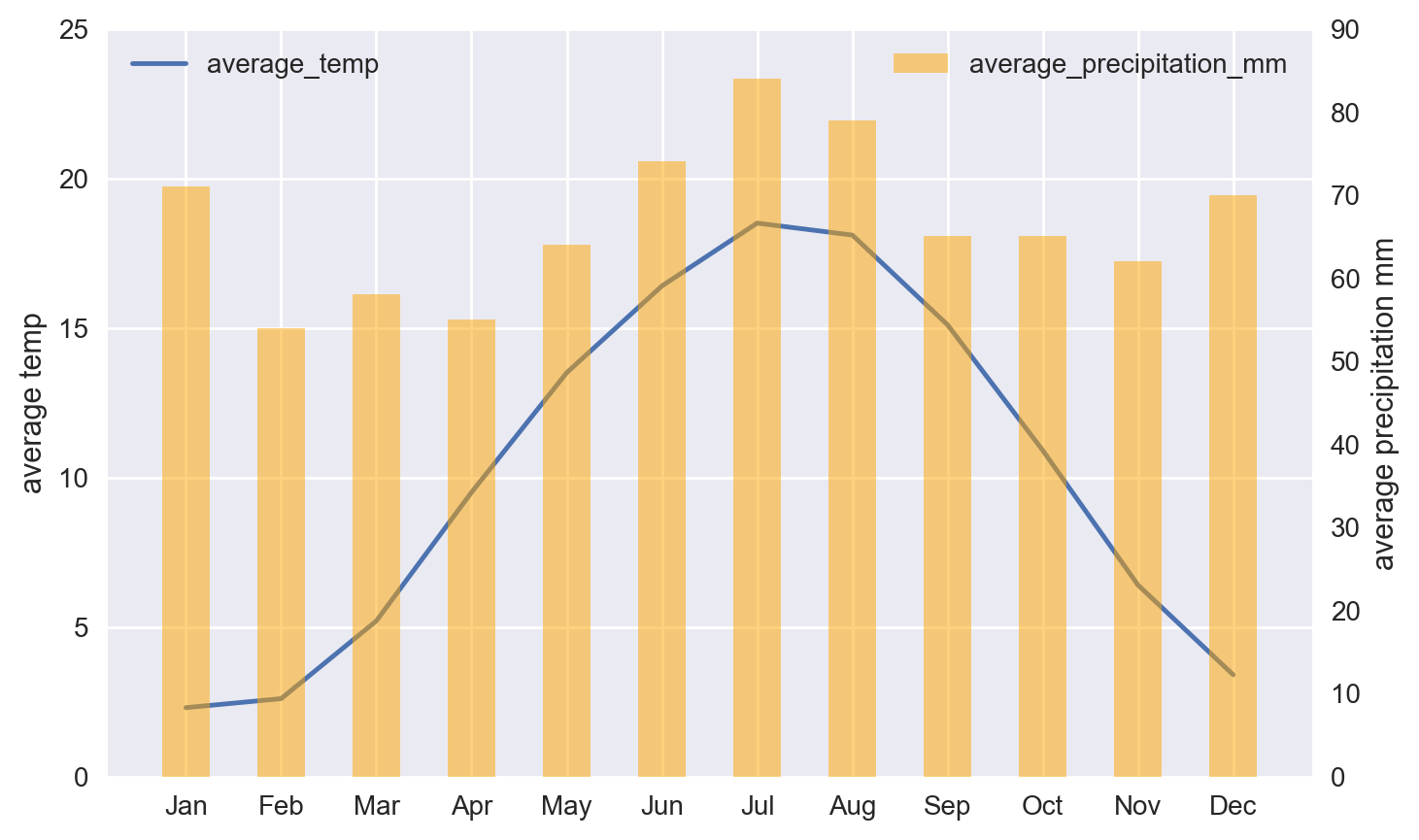
4.5.2. 2. Matplotlib - dual-axis combo chart#
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
# Create figure and axis #1
fig, ax1 = plt.subplots()
# plot line chart on axis #1
ax1.plot(x, average_temp)
ax1.set_ylabel('average temp')
ax1.set_ylim(0, 25)
ax1.legend(['average_temp'], loc="upper left")
# set up the 2nd axis
ax2 = ax1.twinx()
# plot bar chart on axis #2
ax2.bar(x, average_precipitation_mm, width=0.5, alpha=0.5, color='orange')
ax2.grid(False) # turn off grid #2
ax2.set_ylabel('average precipitation mm')
ax2.set_ylim(0, 90)
ax2.legend(['average_precipitation_mm'], loc="upper right")
plt.show()
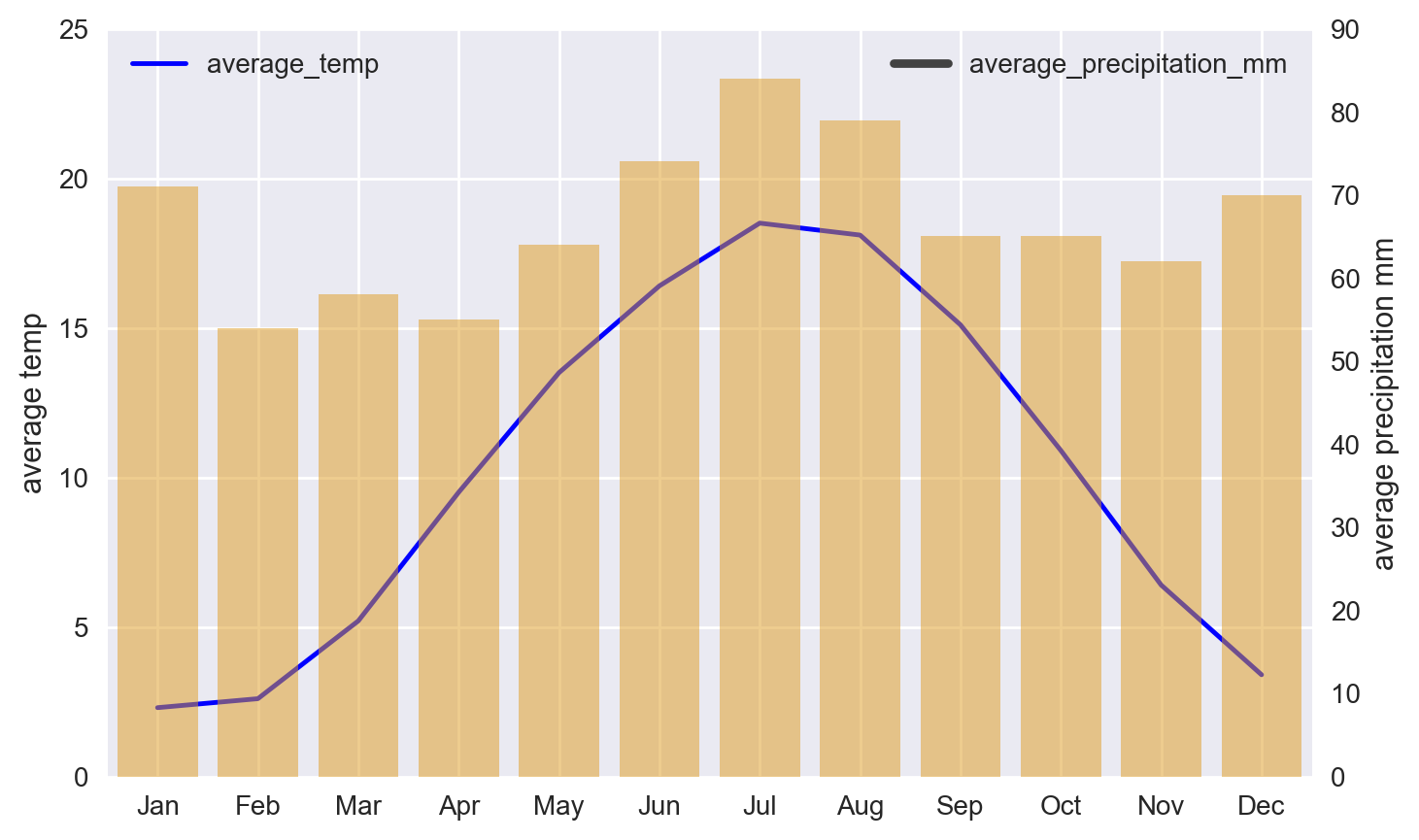
4.5.3. 2. Seaborn - dual-axis combo chart#
bremen_climate_df = bremen_climate.reset_index()
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
# plot line chart on axis #1
ax1 = sns.lineplot(
x=bremen_climate.index,
y='average_temp',
data=bremen_climate,
sort=False,
color='blue'
)
ax1.set_ylabel('average temp')
ax1.set_ylim(0, 25)
ax1.legend(['average_temp'], loc="upper left")
# set up the 2nd axis
ax2 = ax1.twinx()
# plot bar chart on axis #2
sns.barplot(
x=bremen_climate.index,
y='average_precipitation_mm',
data=bremen_climate,
color='orange',
alpha=0.5,
ax = ax2 # Pre-existing axes for the plot
)
ax2.grid(False) # turn off grid #2
ax2.set_ylabel('average precipitation mm')
ax2.set_ylim(0, 90)
ax2.legend(['average_precipitation_mm'], loc="upper right")
plt.show()
bremen_climate
| average_temp | average_precipitation_mm | |
|---|---|---|
| Jan | 2.3 | 71 |
| Feb | 2.6 | 54 |
| Mar | 5.2 | 58 |
| Apr | 9.5 | 55 |
| May | 13.5 | 64 |
| Jun | 16.4 | 74 |
| Jul | 18.5 | 84 |
| Aug | 18.1 | 79 |
| Sep | 15.1 | 65 |
| Oct | 10.9 | 65 |
| Nov | 6.4 | 62 |
| Dec | 3.4 | 70 |
4.5.3.1. Fix legend color issue#
import matplotlib.patches as mpatches
# plot line chart on axis #1
ax1 = sns.lineplot(
x=bremen_climate.index,
y='average_temp',
data=bremen_climate,
sort=False,
color='blue'
)
ax1.set_ylabel('average temp')
ax1.set_ylim(0, 25)
ax1_patch = mpatches.Patch(color='blue', label='average temp')
ax1.legend(handles=[ax1_patch], loc="upper left")
# set up the 2nd axis
ax2 = ax1.twinx()
# plot bar chart on axis #2
sns.barplot(
x=bremen_climate.index,
y='average_precipitation_mm',
data=bremen_climate,
color='orange',
alpha=0.5,
ax = ax2 # Pre-existing axes for the plot
)
ax2.grid(False) # turn off grid #2
ax2.set_ylabel('average precipitation mm')
ax2.set_ylim(0, 90)
ax2_patch = mpatches.Patch(color='orange', label='average precipitation mm')
ax2.legend(handles=[ax2_patch], loc="upper right")
plt.show()
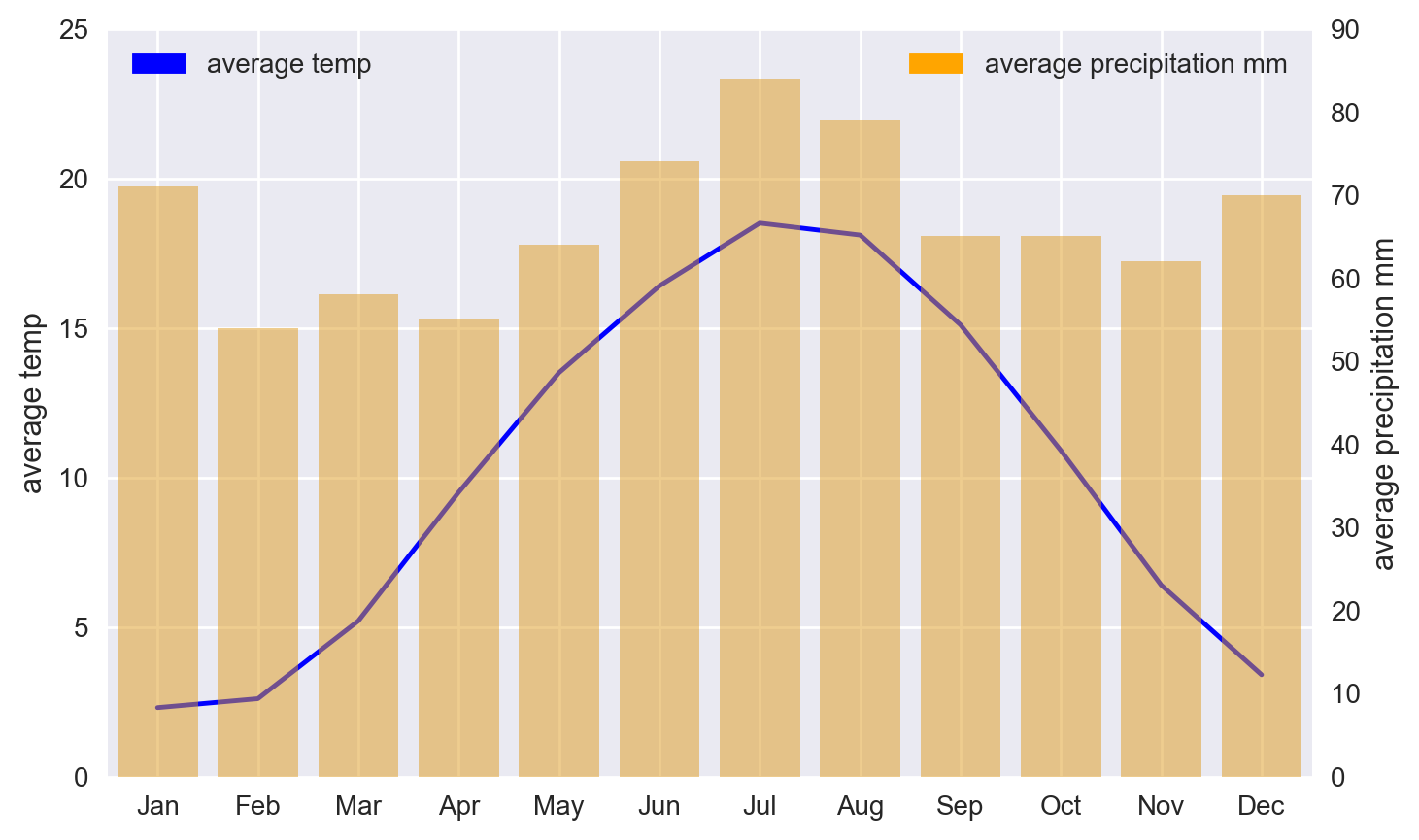
4.5.4. 3. DataFrame plot#
# Create the figure and axes object
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
# Plot the first x and y axes:
bremen_climate.plot(
use_index=True,
kind='bar',
y='average_precipitation_mm',
ax=ax,
color='orange'
)
# Plot the second x and y axes.
# By secondary_y = True a second y-axis is requested
bremen_climate.plot(
use_index=True,
y='average_temp',
ax=ax,
secondary_y=True,
color='blue'
)
plt.show()
4.5.5. Thanks for reading#
This is a Notebook for the medium article Creating a dual-axis Combo Chart in Python
Please check out article for instructions
License: BSD 2-Clause
